The Facts of the Case In the case of Hayford Ofosu Amaning v. The Republic[i], the High Court had tried summarily an accused person who was charged with robbery and attempted murder. The accused was convicted on both counts and sentenced to a term of twenty-five years. The sentences were to run concurrently. Consequently, the accused...
Category: Criminal Law
The Money Laundering Conundrum: Know Ghana’s Legal Nuances and Perspective
Introduction Money laundering known in latin “pecuniam lavare” simplistically is the process of disguising, masking, masquerading and concealing the source and/or true nature of money obtained through illegal means.The Black’s Law Dictionary1 defines money laundering as the act of transferring illegally obtained money through legitimate people and/or accounts so that its original source cannot be traced. The Anti-Money Laundering Act2 provides...
Mental Health and Criminal Law in Ghana
Mental health issues have dominated global health conversations over the years, mainly due to the increasing rates of suicide, depression and substance abuse, especially among the youth. Mental health encompasses the emotional and psychological wellbeing of a person. In Ghanaian criminal legislation, there are offences that border on the affected mental health of accused persons at...
The Implications of Lost or Missing Record of Proceedings
In the Supreme Court case of Jones Bonuah @ Eric Annor Blay v The Republic, the appellant appealed against (a) his conviction for robbery and (b) the decision of the Court of Appeal dismissing his appeal before them on grounds, among others that, the record of appeal from the trial High Court produced by the...
Right to Privacy in Criminal Matters
The right to privacy is a fundamental human right. Article 18, clause 2 of the 1992 Constitution provides that: “No person shall be subjected to interference with the privacy of his home, property, correspondence or communication except with law and as may be necessary in a free and democratic society for public safety or for...
GES, the Law and the Ban on Corporal Punishment
The Ghana Education Service (GES) in 2017 officially banned all forms of corporal punishment of children in schools in Ghana as part of efforts aimed at promoting a safe and protective learning environment for children.[1]The GES directed in January 2019 that a Positive Discipline Toolkit which gives alternatives to corporal punishments be adopted by all...
When Changing Your Mind Means Nothing
It has been said that only a fool never changes his mind. However, in our criminal jurisprudence, setting certain actions in motion without completing them may constitute an offence regardless of the change of mind. These offences are referred to as inchoate offences. This means that a full-blown offence does not need to have been...
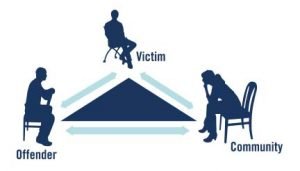
Victim-Offender Mediation and the Criminal Justice System
Under the criminal justice system, a crime is regarded as an offence against the state and not the victim.[1]The state steps into the shoes of the victim and prosecutes the offender. In the end, the state focuses on punishing the offender to either pay a fine to the state or commit the offender to a...
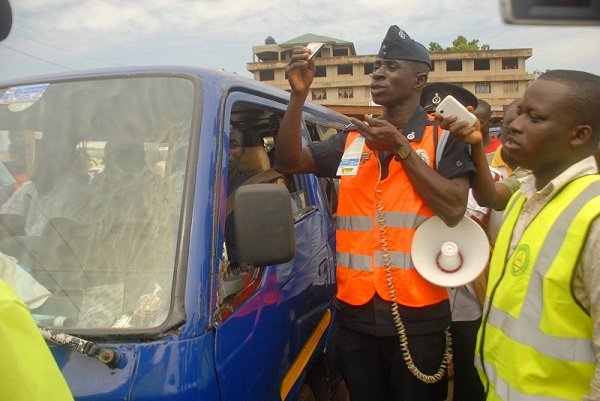
What Does the Law Say – “Traffic Police: Things to Remember”
A few weeks ago, I saw eleven facts on traffic rules which sought to educate users of the road, particularly drivers. This was virally shared on social media platforms and had no source. In this article I will attempt to correct the position of the law as it applies in Ghana with particular reference to...
Nolle Prosequi and Withdrawal
Article 88(3) of the 1992 Constitution gives power to the Attorney General to initiate and conduct all prosecutions on behalf of the state. In the conduct of this duty, the Attorney General is given certain powers. Two of such powers are the power of nolle prosequi and withdrawal. This piece looks at how these two...